Let it never be said that nature has run out of surprises. Or that science has run out of discoveries. Exosomes are extracellular vesicles (EVs) first described as such 30 years ago and since implicated in cells, cell communication and the transmission of disease states. Fundamental questions about their biology remain unanswered. Here is the current definition and some of the outstanding issues in exosome biology –
The exosome is composed of all of the exons within the genome, the sequences which, when transcribed, remain within the mature RNA after introns are removed by RNA splicing. This includes untranslated regions of mRNA, and coding sequence (or CDS). Exome sequencing has proven to be an efficient method to determine the genetic basis of more than two dozen Mendelian or single gene disorders.
Exosomes and the Future of Erectile Dysfunction Treatment.
Erectile dysfunction, or ED, affects nearly half of men between the ages of 40 and 70 to some extent. Vascular diseases interrelated with aging, hyperlipidemia, smoking, diabetes as well as hypertension, are often linked to erectile dysfunction. Furthermore, injury to cavernous nerves in the penile region “comprises an appreciable number of ED cases.” Other causes of erectile dysfunction include, but are not limited to endocrine disorders, as well as fibrosis of the penile tissue and corporal smooth muscle. Overall, both vasculogenic and neurogenic erectile dysfunctions are linked to the loss of normal cellular function or cell death (apoptosis).
Oral medications such as phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (PDE5is), have clear benefits. Most recently, however, scientists and physicians have been focusing on new, next-generation, novel therapy options as a way to restore natural sexual function. One such treatment option includes Stem-Cell-based Bioactive Factor Therapy.
Stem-cell-based therapies focus on the management of erectile dysfunction “through the protection of the threatened host cells via immunomodulatory effects, and the provision of trophic factors or gene delivery.” In recent years, a number of research studies are supporting the concept that stem cell-based bio-active therapy is potentially the next generation therapeutic approach for erectile dysfunction.
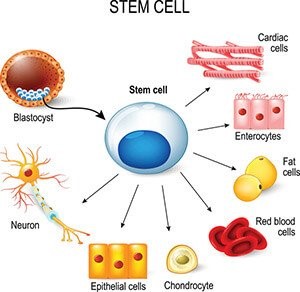
What are Mesenchymal Stem Cells?
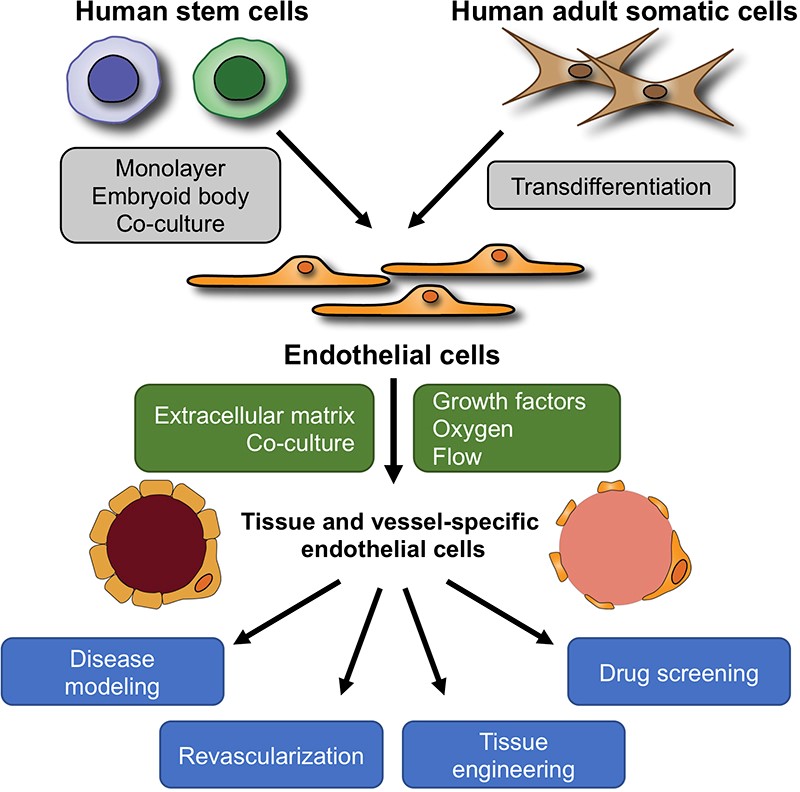
Stem cells differentiate into smooth muscle cells, neurons, endothelial cells and other types of varying cells. Stem cells by definition have the capability of self-renewal, meaning that they can make copies of themselves for an indefinite period, and differentiate into a variety of phenotypes. Stem cells represent great promise for regenerative medicine.” Stem cells can be categorized as either embryonic stem cells (ESCs) or adult stem cells (ASCs). Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are adult stem cells which can be isolated from human and animal sources. The word “Stem Cells” more correctly known as “Mesenchymal Stem Cells” (MSCs) were termed MSCs secondary to their innate ability to duplicate while maintaining the attribute of multi-potential lineage
What are Bioactive Factors and EVs?
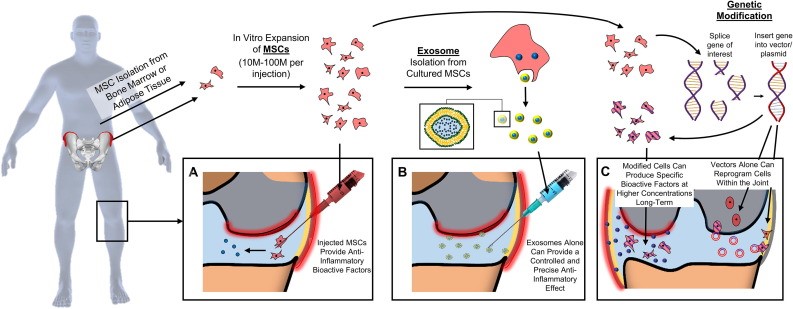
MSCs are able to secrete “Bioactive Factors”, such as exosomes and other extracellular vesicles (EVs), which aid in modulating the immune system, improve the standard rate of healing injured tissues and reduce inflammation. Stem Cell Bioactive Factors consist of nanoparticles which are released from the membranes of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs). These nanoparticles contain over “200 Growth factors, Cytokines and Nucleic Acids which support healthy cell-to-cell communication and are responsible for the therapeutic effects observed in regenerative medicine,” as well as perform a critical role in important processes such as immune responses, homeostasis maintenance, and more.
Microvesicles, an important EV, may “change functional target cells by delivering intracellular proteins.” For example, MVs released from endothelial cells can promote the regeneration through transfer of growth factors and their activators. MSC-derived EVs (MSC-EVs)-based stem cell therapies are easier to manage and safer “due to their inability to directly form tumors.”
Mesenchymal Stem Cell’s Bioactive Factors
Bioactive Factors demonstrate numerous advantages when compared to Mesenchymal Stem Cells:
- Bioactive Factors do not contain DNA as they have no cells therefore there is no risk of a malignant transformation.
- Bioactive Factors contain nanoparticles, which can travel systemically without the risks of clumping.
- Bioactive Factors have the ability to cross the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB) and are able to exert their neurotrophic effects.
- MSCs can be perceived as “foreign” by our own immune system (both innate and adaptive); however, Bioactive Factors are able to evade immune response.
Essentially Bioactive Factors exert far more therapeutic effects than Mesenchymal Stem Cells could.
Therapeutic Effects of Stem Cell Bioactive Factors
Growth factors, cytokines, and nucleic acids within stem cell bioactive factors are catalysts for regeneration as they contribute to tissue and organ repair, alter inflammation, aid in neural communication, improve mitochondrial viability and participate in the alteration of aging cells. Overall, bioactive factors derived from stem cells aid the body in repairing damaged tissues and injuries.
Stem cell bioactive factors have been utilized by medical professionals for a number or varying aspects including, but not limited to, soft tissue repair, and restoring sexual wellness. In regards to men’s sexual health, Exosomes Therapy rejuvenates, repairs, and regenerates damaged penile tissues, aiding in the restoration of erectile function which may contribute to eliminating the need for long term reliance on drugs.
Some Examples of Bioactive (Growth) Factors
- VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors): Aids in the creation of new blood vessels, and in the generation of muscles through bypassing blocked vessels.
- PDGF-BB (Platelet Derived Growth Factor Sub Unit B): Stimulates the healing of soft as well as hard tissues.
- TGF B3 (Transforming Growth Factor B3): Aids in the conversion of inflammatory T cells into anti-inflammatory Regulatory T cells.
- GDF 15 (Growth Differentiation 15): Regulates inflammation and aids in cell repair as well as growth.
How Clinic for Him Sources Bioactive Factors (Exosomes)
Clinic for Him utilizes Exosomes produced from an FDA-registered Tissue Bank which follows strict GMP guidelines and implements as well as maintains FDA regulations. The Tissue Bank sources from the highest quality donors and harvests from the healthiest part of the placenta in order to produce viable MSCs from which secreted Exosomes are collected at the highest point potency. Upon the completion of manufacturing, each batch is sent for third party testing regarding microbiology and other safety protocols.
Clinical Trials Regarding Stem Cell Therapies and Erectile Dysfunction
Exosomes Therapy can utilize varying types of stem cells including MSCs. Exosomes may also treat erectile dysfunction by supporting penile tissue through paracrine or hormone effects such as the “release of repair cytokines triggering endogenous mechanisms of regeneration separate from the transdifferentiating of stem cells into different cell types.” Furthermore, MSCs do not necessarily need to be engrafted within tissue to create a functional and structural response to the therapy administered.
Phase one studies in humans have shown “results in terms of tolerability, safety, and efficacy of use of stem cell transplant for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.” Recent studies have also suggested that the combination shockwave therapy and stem-cell bioactive factors or Exosomes Therapy may decrease cell destruction within the penile corpora region as well as promote the growth of new blood vessels.
A literature review from ScienceDirect regarding the efficacy of stem-cell bioactive factors therapy revealed that five previously completed human clinical trials did show promise for the therapy as “being a restorative treatment option for erectile dysfunction,” the five studies included in the literature review utilized different types of stem cells, including various mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). A total of 61 patients were included in the five studies, with mean ages of men being between 50 and 70 years. The literature review found that the majority of the five studies suggested improvement in erectile function and vascular flow in the penile region due to stem cell therapy without the report of serious adverse events occurring during the follow-up period.
Exosomes Therapy may be a paradigm shift in the growing number of treatment options available for erectile dysfunction. Exosomes Therapy has been recognized for its therapeutic properties in regards to aiding in treatment for various conditions including erectile dysfunction. ReGen Therapy embraces the latest in advanced technologies to help men restore erectile function without the use of drugs or the long-term reliance on drugs. Clinic for Him utilizes treatment protocols which are personalized to the individual’s conditions and may combine regimens such as shockwave therapy called ™ Therapy, PRP Injections and Exosomes Therapy. Thanks to a vast amount continuing research and development, Clinic for Him physicians have utilized the most efficacious treatment protocols and continue to be the market leader in the field Erectile Dysfunction.
Clinic for Him’s Optimum Regenerative Solution
Clinic for Him utilizes the latest in next generation revolutionary treatment options for Erectile Dysfunction while upholding to GMP guidelines, and the utmost standards or requirements regarding the utilization of FDA registered tissue procurement organizations for Exosomes Therapy. Clinic for Him utilizes Stem-Cell Bioactive Factors secreted from the membranes of placental-derived MSCs (mesenchymal stem cells) which possess more than 200 growth factors as well as other immune factors which can render considerable therapeutic benefits.
References:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3735142/#bib1
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18286209
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3735142/#bib3
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17254699
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23456256?dopt=Abstract
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3735142/#bib6
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23456256?dopt=Abstract
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16458737
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2016.00024/full
- https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/15/3/4142
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2050052119300964#bib23
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2050052119300964#bib24
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2050052119300964#bib28
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2050052119300964#bib29
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2050052119300964#bib30
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2050052119300964#bib31
- https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1743609517313401
- https://stemcellsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/stem.2445
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/and.12871
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3735142/#bib95
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2050052119300964