What is Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction, also called ED, is the inability to obtain and maintain an adequate erection during sexual intercourse. One out of every ten men will get ED at some point in their life, as it is a common type of male sexual dysfunction. In the US, roughly 30 million men are affected by ED, according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK).
It is essential to recognize that ED is not considered normal or expected at any age and can be associated with various issues that impact both sexual desire and performance. These issues may include difficulties with penile erection, lack of sexual desire, problems with achieving orgasm, and challenges related to ejaculation.
Is ED Related to Aging?
ED does not have to be a part of aging. While some older men may require more stimulation, they should obtain an erection and enjoy intercourse without any assistance.
Moreover, getting an erection less than 20% of the time shouldn’t worry a man. It’s not uncommon, and there’s usually no treatment required when it’s only a sporadic issue. Even so, depending on the person’s medical history and health conditions, failure to obtain an erection more than 50% of the time typically indicates an issue, and medical treatment might be necessary.
It is of huge importance to address the broader context of medical conditions that may contribute to ED, as they can significantly affect overall sexual satisfaction and performance during intercourse
The following graphic shows the percentage of certain medical conditions that may cause erectile dysfunction:
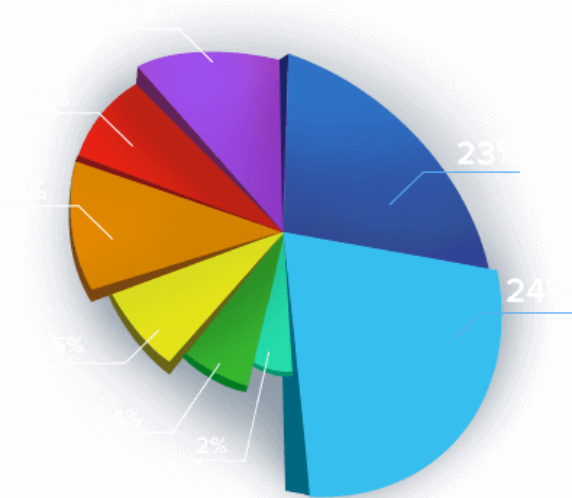
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Medications
- Surgery / Injury
- Neurological Disease
- Endocrine
- Psychological
- Unknown Causes
Erectile Dysfunction Causes:
Psychological Factors
Approximately 10% of erectile dysfunction (ED) cases stem from psychological factors, including uneasiness, sexual performance anxiety, or fear of failure during sexual intercourse.
This form of ED can become self-perpetuating, as repeated unsuccessful attempts can condition the body to release adrenaline even at the mere thought of a sexual encounter. Failing to address this issue in a timely manner can lead to a relentless cycle that is challenging to break.
To tackle psychological ED, a comprehensive approach involving physical examination, assessment of sexual history, and evaluation of testosterone levels is necessary.
The characteristics of psychological erectile dysfunction are:

Erection is only possible if maintained with one partner but not with another.

Lasting erections are only achieved and maintained in the mornings or during masturbation, not during sexual intercourse.

Relationship problems due to poor communication or other concerns.

Being a younger male with unstable relationships or disturbing prior experiences.

Depression, anxiety, or other mental health conditions.

Stress

Erectile Dysfunction Causes:
Physical Factors
The majority of erectile dysfunction (ED) cases, approximately 90%, can be attributed to physical causes, specifically vascular and non-vascular disorders. Vascular diseases alone are estimated to contribute to around 70% of all ED visits.
The occurrence of ED is influenced by the fact that consistent and adequate blood flow is necessary for the penis to achieve a fully erect state. Even a minor decrease in blood flow can create difficulties in attaining an erection.
Consequently, ED pills, recognized as highly effective medical treatments, work by increasing blood flow in the penile blood vessels. This improvement in blood flow enables individuals to achieve erections and enhances their sexual and erectile function.
ED is also a condition characterized by ineffective blood vessel function and is referred to as “vascular insufficiency,” which is connected to the prevalence of erectile dysfunction concerning sexual health, not being able to maintain a normal erection and issues with nerve function. The following are some of the risk factors for ED:

Diabetes or Diabetes Mellitus.

Hypertension (high blood pressure).

High blood cholesterol.

Cardiac diseases or cardiovascular events.

Smoking.

Poor overall circulation.

Chronic use of illicit drugs.
Also, evidence suggests that over 200 prescription drugs may cause, contribute to, or aggravate ED. Even so, don’t stop taking your prescriptions unless otherwise directed by your physician. Still, it’s essential to be on the lookout for any possible damage that may come directly from your medication.
Other physical factors for erectile dysfunction or causes include:

Hormonal shortages that are caused by testicular disease, liver disease, or thyroid issues.

Multiple sclerosis, stroke, and Parkinson's disease (neurological issues).

Heart diseases, such as coronary artery disease.

Trauma to the pelvic area as a result of some forms of surgery, radiation therapy, or car accidents that result in injured pelvic nerves or arteries.

Chronic diseases such as liver diseases, chronic kidney diseases, and so on.

Peyronie's plaque, also known as Peyronie's disease, which is a rare disorder characterized by severe fibrosis in the penile tissue.
Nevertheless, it is not uncommon to notice ED in a person who is otherwise physically and psychologically well. Some studies have proposed that penile circulation is by nature very delicate since it’s an end-artery. With age, obstructions to the blood flow are more common. It usually does not matter, but in older men, it might mean there’s not enough blood flow to the penis during sexual arousal.
Adverse Effects On Daily Life
Erectile dysfunction can induce or exacerbate psychological issues like low motivation, feelings of inadequacy, irritation, denial, and low self-esteem, even leading to mental health issues such as depression. As a result, if left untreated, ED can harm personal, family, and commercial relationships.
How Important Is It to Treat Erectile Dysfunction Proactively?
Erectile dysfunction, like any other medical ailment, is frequently best treated if it’s done as soon as possible. Here are three main reasons to consider treating your erectile dysfunction:
- Diagnosing and resolving the underlying issue frequently helps prevent additional deterioration, which is a natural development of the ailment.
- The inactivity of an organ can result in progressive loss of function due to the progressive loss of healthy tissue. This is known as “disuse atrophy,” and it is especially significant in the case of penile health. Use your penis!
- ED is more than a sexual issue. Satisfying sex life can lead to increased pleasure in many other areas of life, such as social, family, and professional situations.
Is ED related to Venous Leak?
Millions of men worldwide experience erectile dysfunction (ED) nowadays. Even though it’s uncommon, this subgroup of men may experience a venous leak or venogenic erectile dysfunction.
Men who have venous leaks in their penile tissue, which result in mild erections, are said to have this sort of sexual dysfunction. Contrary to the majority of erectile dysfunction cases, this kind of condition doesn’t acutely worsen as a man ages.
Instead, young men with venogenic erectile dysfunction either have the illness from birth or acquire it as they become older, taking it with them throughout their lives.
Overall, medical professionals still find the venous leak to be a medically puzzling illness. However, it can be crippling to deal with and negatively impact a man’s sex life
How is Erectile Dysfunction treated?
There are many options for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients. Depending on severity as well as any underlying causes, here are a few treatment options that can be explored for erectile dysfunction:
- Oral Medication (Sildenafil (Viagra), vardenafil (Levitra, Staxyn), tadalafil (Cialis) and avanafil (Stendra).
- Daily use of low-dose PDE-5 inhibitors
- Penile Injection Therapy (ICI, intracavernosal Alprostadil)
- Penile Implant/Penile Prosthesis
- Testosterone Therapy (when blood tests reveal low testosterone levels)
- Vacuum Device for Erection/ Vacuum Pumps
- Surgery
When to See a Doctor
If you’re having trouble maintaining an erection or you’re not experiencing good sexual stimulation, seeing your primary care physician is an excellent first step. Consult a medical professional if any of the following apply to you:
- You are concerned about the quality of your erections.
- You are experiencing other sexual difficulties, such as early or delayed ejaculation.
- You have diabetes, heart disease, or another recognized health problem that is perhaps linked to erectile dysfunction; nonetheless, you are still unable to achieve and maintain an erection.
Trust Clinic For Him and Let us Help You!
From non-invasive ones like oral medication and shockwave therapy to surgical options like penile implants to vacuum erection devices, our team of health professionals at Clinic for Him will help in choosing the best option for you! More information regarding erectile dysfunction treatment options can be found on our erectile dysfunction treatment page.
See More Resources
If you are looking to improve or restore your sexual health, talk to a Clinic for Him physician to see how they can help.
See More Resources
If you are looking to
improve or restore your
sexual health, talk to a
Clinic for Him physician to
see how they can help.